COMPUPLAST® Virtual Extrusion Laboratory™ - Rubber & TPE Extrusion
The COMPUPLAST® Rubber & TPE Extrusion Package™ can be used for the design and optimization of virtually any rubber and/or thermoplastic olefin extrusion process including co-extruded profiles. It can be used to develop optimized profile dies for maximum production rate, estimate extruder performance and to optimize calibration and cooling systems.
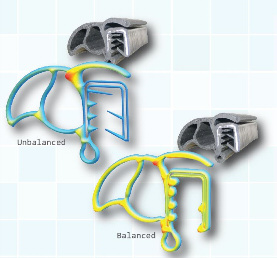
The COMPUPLAST® Rubber & TPE Extrusion Package™ can help the user visualize the material behavior anywhere inside the process. It also allows for adjustment of the die geometry to get balanced flow inside the die to achieve the desired material distribution at the die exit. The analysis can include the effect of moving internal walls, which occur when metal supports are used in the profile.
The die flow balancing can be performed either manually or with an optional Automatic Flow Balancing™ feature, which automatically finds the shape of the die channels that optimizes the material distribution throughout the die. The balancing is based mainly on channel gap adjustment and, if it is really necessary, balancing by channel length can also be employed.

Experience has proven that a die designed by COMPUPLAST® approach is much less sensitive to variations in process conditions (material lot variations, line speed changes, different extruders etc.) and maximizes the production rate.
With the Rubber & TPE Extrusion Package the user can easily avoid the heavily unbalanced flow that occurs during the typical initial die development and thereby achieve the desired profile shape much sooner.
The COMPUPLAST® Virtual Extrusion Laboratory™ for Rubber & TPE Extrusion consists of several modules that can be purchased individually, or in combination, to simulate the various components in a Rubber & TPE Extrusion Process.
The applicable VEL™ Modules are:
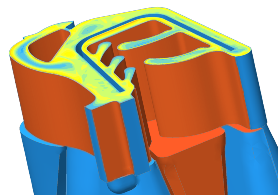
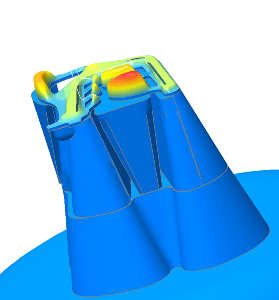
The VEL™ Rubber & TPE Extrusion Package can help the user understand/solve the following problems:
- unbalanced flow
- poor surface quality
- avoiding early cross-linking
- poor final thickness distribution
- profile deformation (bending, warping) during cooling
- performance such as surging, material overheating, material degradation and burning
- problems related to the extruder
- optimizing microwave heating
The package can also show how efficiently and evenly (or unevenly) the product is cooled and if there is a tendency for bending or warping (due
to uneven shrinkage) during cooling.
